The Akkadian Civilization as the First Mesopotamian Empire
- Подробности
- 1095
The Akkadian Civilization is regarded as the first great empire of the broader Mesopotamian world. Founded by Sargon of Akkad in the 24th century BC, it united the Sumerian city-states and surrounding regions under one centralized rule. The very name Akkad became synonymous with imperial power and marked a new stage in the development of Mesopotamian culture.
The Akkadian Civilization
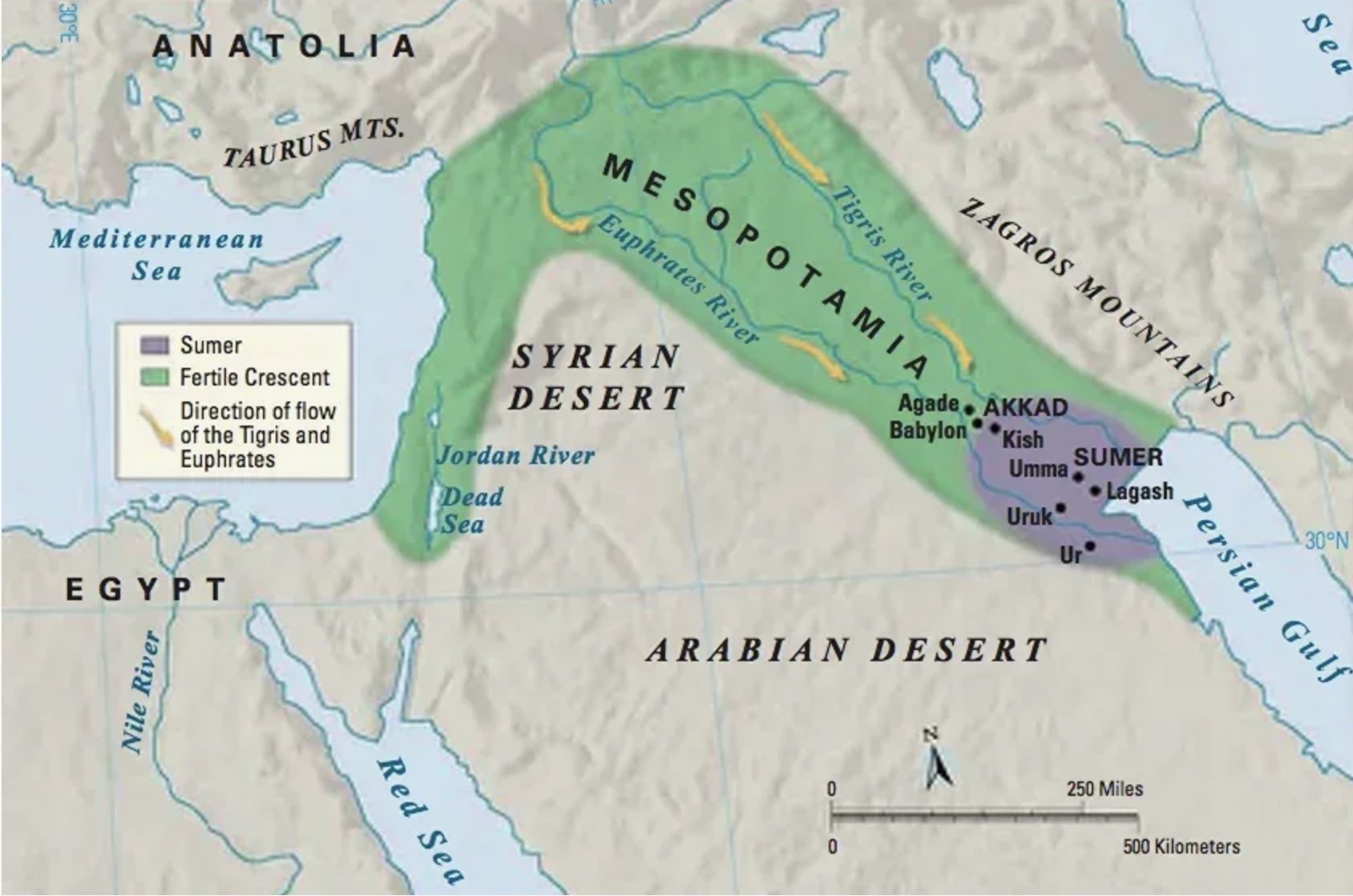
The Akkadian civilization is regarded as the first great empire in Mesopotamian history. Founded by Sargon of Akkad in the 24th century BC, it united the Sumerian city-states and surrounding regions under one centralized rule. The very name of the city, Akkad, became synonymous with imperial power and marked a new stage in the development of Mesopotamian culture.
Emerging in central Mesopotamia, the Akkadians established their capital at Akkad and expanded their control across the land between the Tigris and the Euphrates. For the first time, Mesopotamia was ruled as a single political entity. They preserved many Sumerian traditions but introduced their own Semitic language, which became the lingua franca of the ancient Near East for centuries.
One of the Akkadians’ greatest contributions was the creation of the first centralized administration and taxation system. They appointed governors over conquered cities, standardized laws and trade practices, and strengthened royal authority. Royal inscriptions and monuments glorified their kings, especially Sargon and his grandson Naram-Sin, who even declared himself “King of the Four Quarters of the World.”
The Akkadians continued to use cuneiform writing but adapted it to their own language. They supported art, literature, and religion, blending Sumerian gods with their own beliefs and emphasizing the divine nature of kingship. Their armies campaigned far beyond Mesopotamia, reaching the Mediterranean coast and the Persian Gulf, which expanded trade and cultural contacts.
Although the Akkadian Empire lasted only about two centuries, it left a profound legacy. Internal strife and invasions by the Gutians eventually weakened it, but its model of centralized government, imperial ideology, and widespread use of the Akkadian language shaped all later Mesopotamian civilizations. That is why historians view the Akkadian civilization as the first empire and a crucial turning point in Mesopotamian history.
LISTEN TO THE TEXT




 Как правильно изучать английский язык по карточкам (статьи)
Как правильно изучать английский язык по карточкам (статьи)